HLA
AROUND SPORT – SWIMMING COURSE
- Brief description
- Context and needs
- Activities and rules
- Location, environment and equipment
- Method
- Side Activities
- Target
- Impact
The swimming course is done in an educational pool (about 80 cm high) in which all children approach, through the game, to move in the element of water: move, know the dangers and get pleasure from the activity. This will allow the child to relate to the water in a pleasant and independent way in every area (other pools, sea, etc.).
The instructors teach an emotional education that allows the child to reach the technical domain. This will allow the child to live serenely and pleasantly with a unique sensory experience.
The swimming course in addition to the relationship child- instructor, child- water, tries to develop a job that goes to create group dynamics determinant for the growth of a good sportsman and not only. Through the concept of collaboration we learn the relationship and the comparison with all the diversities learning to help and to be helped.
The aquatic experience is a unique and ancestral sensory experience. The water element is containment, lowering in a very evident aggressiveness. Being proposed in the educational pool (low pool) the child feels safer.
For children with autism spectrum, the swimming course in the swimming pool is an excellent container of motor, sensory and socio-affective experiences.
The activity develops at different times:
“Reception”
The instructor welcomes the children in the pool with the “5”, then accompanies them by the pool. Kneeling in front of the child in case of need (especially 3-6 years). We avoid hands in pockets, having arms folded and using mobile phones. Smiling face. Happy look. Sweet, cheerful, reassuring tone of voice. Also the tone of voice determines “freedom”. Try to communicate, if necessary, kneeling at child height. Request the “5”. N.B. Sometimes the “physical” request of the “5” may initially be too intrusive. We need to create the “emotional” space in which the child can feel safe to move.
Different settings of RECEPTION
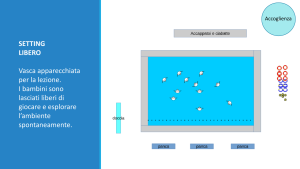
Welcome in a free setting: swimming pool “set” for the lesson. Children are left free to explore the environment spontaneously.
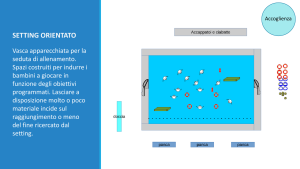
Reception in oriented setting
Swimming pool “set” for the training session. Spaces built to orient children to play according to the objectives programmed. Leaving much or little material available affects the final learning result.
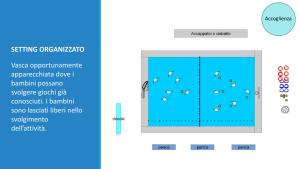
Reception in organized setting
Swimming pool “set” where children can play games is already known. Children are left free in the interpretation of the activity.
Game 1: THE GAME OF THE MONKEY
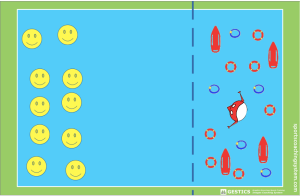
The monkey (educator) defends its territory from the baby monkeys who want to take possession of all the fruits it contains. The baby monkeys that are caught:
- become monkeys
- will have to remain still waiting for them to be freed by a specific motor gesture.
- Other modes
GAME 2 – Pirates to the rescue
STARTING SWIMMING – ADVANCED (WATER)
Name: Pirates to the rescue
Material: objects of all kinds
Exercise duration: 5 -10 min. Each round lasts about 3 minutes.
Number of children: 6 -12
Theme: Two teams are on opposite sides of the tank and have the same number of treasures inside the chest. Every child must try to steal an object from the opponent’s chest. To the outward always making jumps to dolphin ( or with other techniques on which you are working), to the return (with the stolen treasure) always with movement to crawl (or to pleasure).
Variants:
- Using the tablet to move.
- Entry of a Commander (child who starts from outside a tub with a circle in his hands) who can stop pirates ONLY when they have a treasure in their hands.
- Stop = touch the child with the circle. The arrested child will have to stop with open legs or stay still. To free pass under the legs or find a mode preparatory to the Game or technical purpose.
- Use of coloured balloons or other materials with a different finish to material counting.
GAME 3 – The bell of Santa Claus.
Different materials are distributed in the bottom of the pool. In addition to these will be hidden the bell of Santa Claus. While the Elf ( Instructor ) hides it, the other Elf ( instructor ) keeps them imprisoned with hands on the wall turned to do a static analytical exercise. At the start they have to look for the bell. The first one who finds it rings.
Variant:
- Vary the technical/motor delivery to the sound of the bell.
- Playing in pairs: a child walks and takes the hand of the partner who swims.
Treasure Hunt: Pairs are formed. The instructor throws the headbands at the bottom of the pool and gives directions before looking at them together (collaboration between disabled and disabled). Then he asks a child to pick them up with his foot and give them to his partner. They take them back to their own container outside the pool.
Give a score both on the number of objects collected and on the collaboration (directing the score towards the child who collaborates with the disabled child). Explore different evolutions of the game where collaboration is predominant.
Exit: If we have material in the water we can use the countdown to collect the material. ” Round Water” (circle in the water). Remember at the exit to give the ” 5 ” .
ROLES OF THE SPORTS OPERATOR IN THE GAME
Operator’s step in inclusive key:
- play with the child while maintaining physical contact
- play with the child supporting him with his voice and with his eyes remaining inside the playing space
- supports the child with voice and eyes, staying out of the playing space
follows the child only with the eyes, remaining outside the game space intervening only if necessary with reinforcement.
- Educational pool (about 80 cm high)
- Balloons, balls, hoops and different soft tools.
- Include max 1 or 2 disabilities in each group.
- Obliquity: all participants must experience the perception of the psychophysical well-being that motor activity produces. Every athlete must have the opportunity to train to the maximum of his potential, living some moments of slowdown as wealth.
- Fairness: Create exercises in which the final gratification is present (for example goal shooting) and everyone can have the chance to reach it. Example: The game of colored doors allows everyone to score with their potential.
- Tool: Use the game in all its forms, as a “prince” learning tool. (G.P, G.E., G.S, G.P.)
- Share with all the technical staff, society and family the sporting and social goals of the inclusive activities.
- “Free water”: an event in which parents and children play together in the water. This also helps families to live an inclusive experience.
- Cultural conferences of education to inclusion. Calendar moments in which you share with other people experiences, results and future goals of inclusive sport.
Males and females from 6 to 8 years.
Exponential growth of:
- Emotional intelligence (empathy)
- Know how to manage the needs of the disabled player
- Mathurity (both of non disabled and disabled children)
- Happiness and satisfaction
Increased sensitivity in collaborative actions by athletes during the match
Lowering moments of aggression.
Fair Play.
PlayInc Key Aspects
Swimming satisfies the key aspect of Playinc because water allows a unique sensory experience that activates all motor-cognitive-emotional abilities. The instructor makes the child live a moment of play through a guided exploration approach in a different setting where the child feels joy, containment and relaxation.
The water setting has a strong individual characteristic but in the water we can propose many group games stimulating collaboration and inclusion. The instructor is strongly stimulated to create new modes of activity helped by the plus value that the water returns.
Collateral activities help disabled people’s families to create new links between them and to be included, because discrimination doesn’t stop at the disabled child but falls on all the sociality of family.
Contact the organisation
Contact

Name: Around Sport (AS)
Website: https://www.around-sport.it
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/aroundsport.it
E-mail: internationalaffairs@aics.info
